Dissertation代写辅导参考:Leadership & Operations Management of Audi

Dissertation代写辅导参考-奥迪领导层与运营管理。本篇内容是本站提供的dissertation代写辅导参考节选,该篇dissertation是为奥迪董事和高级管理人员编写的,并应其要求,旨在调查运营管理的不同方法/实践以及组织的整体绩效。奥迪公司的重点是理解运营管理在组织环境中的价值;以及有效的运营效率如何帮助企业成功实现业务目标。Dissertation探讨了不同理论和方法/实践模型在奥迪公司工作环境中的应用;所产生的信息/证据在上下文中是全面的。下面就一起来看一下这篇dissertation代写辅导参考节选内容。

Organisation: Audi AG, Head Quarters: Ingolstadt, Germany, Chairman of the Board of Management: Prof Rupert Stradler (Audi, 2016)组织:奥迪公司,总部:德国因戈尔施塔特,管理委员会主席:Rupert Stradler教授
This dissertationhas been conducted for and requested by the Directors & Senior Management Personnel of Audi AG, to investigate the different approaches/practices towards Operations Management, the overall performance of the organisation. Key emphasis has been placed upon understanding the value of Operations Management within the organisational context at Audi AG; and how effective operational efficiencies can aid businesses to successfully achieve business objectives. The application of different theories and models of approach/practice towards contrasting situations within the Audi AG working environment has been explored; for the resulting information/evidence to be contextually comprehensive.
Methodology 方法论
The information contained within this Briefing dissertation has been obtained primarily through secondary research techniques including web-based research, academic journal reading and published books and articles. The reasons behind this, are that it is particularly problematic gaining primary research information from Board Level Directors & Senior Managers due to time constraints, thus much of the information is obtained through organisational publications. However, primary research was utilised on occasions where greater depth was needed or the required information was not obtainable through other methods.
本篇dissertation所载信息主要通过二次研究技术获得,包括网络研究、学术期刊阅读以及出版的书籍和文章。这背后的原因是,由于时间限制,从董事会级别的董事和高级经理那里获得主要研究信息尤其困难,因此大部分信息都是通过组织出版物获得的。然而,在需要更大深度或无法通过其他方法获得所需信息的情况下,使用了初步研究。
Results 结果
2.1 Audi AG Organisational Structure 奥迪公司组织结构
Audi AG (Audi) was ‘historically’ established in 1910 by founder August Horch in Zwickau (Central-Eastern Germany). Audi AG operates and distributes cars worldwide, manufacturing cars in 11 Production Facilities across 9 countries in Europe, Asia, North America and South America. Audi AG Group currently employees 84,435 members of staff (November 2016) with a revenue of 58.42 Billion EUR (Full year ended 31 March 2016) & Chairman of the Board of Management is Prof Rupert Stradler (Audi, 2016).
奥迪公司由创始人August Horch于1910年在茨维考(德国中东部)“历史性”成立。奥迪公司在全球范围内运营和分销汽车,在欧洲、亚洲、北美和南美9个国家的11个生产工厂生产汽车。奥迪集团目前拥有84435名员工(2016年11月),收入584.2亿欧元(截至2016年3月31日的全年),管理委员会主席为Rupert Stradler教授。
Audi AG is categorised as a large multinational organisation and is a constituent of the Frankfurt Stock Exchange with a current share price as of COP (close of play) on 8th December 2016 at‚¬604.62 EUR (Frankfurt Stock Exchange, 2016). Audi AG has many subsidiary companies including Lamborghini, Italdesign Giugiaro, Audi Brussels and Audi Hungaria Motor Kft; with also an overriding parent organisation of Volkswagen Group sitting above Audi AG in hierarchy. (Audi, 2016)
奥迪公司被归类为大型跨国组织,是法兰克福证券交易所的组成部分,截至2016年12月8日COP,其当前股价为604.62欧元。奥迪公司旗下有兰博基尼、意大利设计公司Giugiaro、奥迪布鲁塞尔和奥迪匈牙利汽车公司;此外,大众汽车集团的上级组织在层级上高于奥迪公司。
2.1.1 Organisational Management Structure 组织管理结构
Audi AG is a vast organisation with a Management Matrix/Structure that consists of many layers across various business functions and geographical prominence. “The corporate management of Audi AG draws on its expertise and leadership to promote the interests of more than 80,000 employees, the Audi shareholders and the Audi customers around the globe. The managers of Audi AG form the basis for responsible corporate management.” (Audi, 2016) Prof Rupert Stradler (Chairman of the Board of Management) is at the summit of the Board of Management and is responsible for the forward planning of the organisation, coupled with the performance of his appointed Board of Management. Beneath the Chairman, the Board of Management consists of Board Members responsible for the performance of specific business functions within the organisation globally; these include: Procurement, Human Resources & Organisation, Finance & IT, Sales & Marketing and Production & Logistics. The full list of Audi AG Board Members is shown in Appendix A. Beneath the Board of Management, Audi AG is dissected depending on Geographical Area within each discipline. For example, European Sales & Marketing Director & North American Production & Logistics Director; these individuals will report up to the relevant Board Member. The regions are once again split up depending on individual plants/locations and the Management Structure continues this trend throughout the organisation. See [Figure 1] Audi AG Company Organogram for further clarification of the Organisational/Management Structure within the organisation. (Audi, 2016)
本篇dissertation认为奥迪公司是一个庞大的组织,其管理矩阵/结构由多个层次组成,涵盖各种业务职能和地理位置。“奥迪公司的企业管理层利用其专业知识和领导力,促进了全球80000多名员工、奥迪和奥迪客户的利益。奥迪公司的管理人员是负责任的企业管理的基础。“Rupert Stradler教授出席了管理委员会的峰会,负责组织的前瞻性规划,以及他任命的管理委员会的绩效。在董事长之下,管理委员会由董事会成员组成,负责在全球范围内履行组织内的特定业务职能;其中包括:采购、人力资源与组织、财务与IT、销售与营销以及生产与物流。奥迪公司董事会成员的完整名单如附录A所示。在管理委员会之下,奥迪公司根据各专业的地理区域进行了划分。例如,欧洲销售与市场总监、北美生产与物流总监;这些人将向相关董事会成员报告。区域再次根据各个工厂/地点进行划分,管理结构在整个组织中延续了这一趋势。参见[图1]奥迪公司组织结构图,以进一步了解组织内的组织/管理结构。
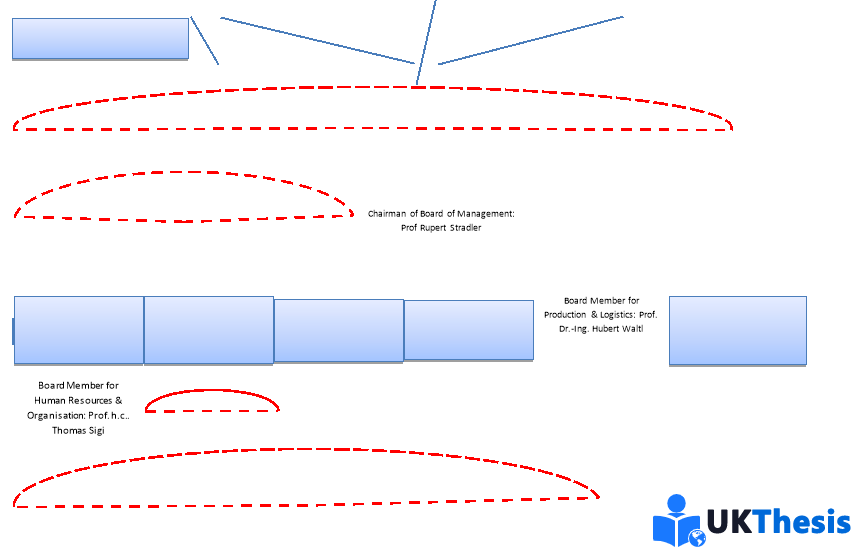
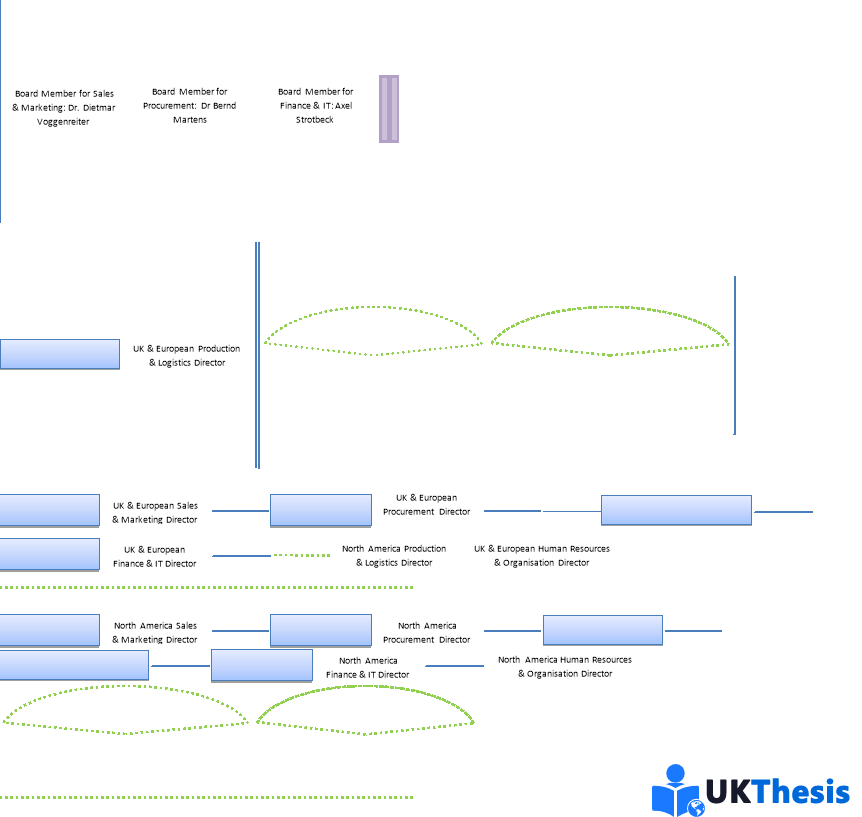
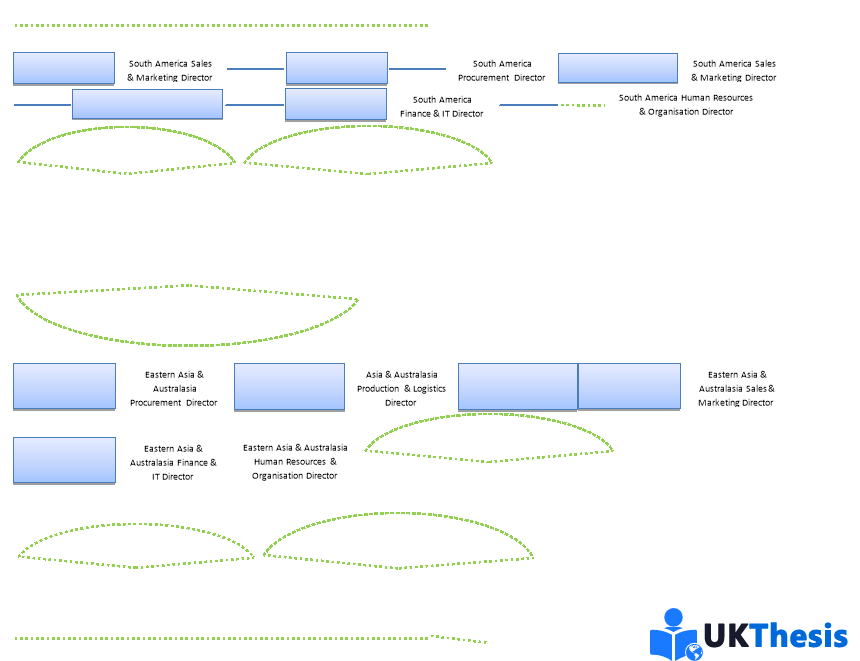
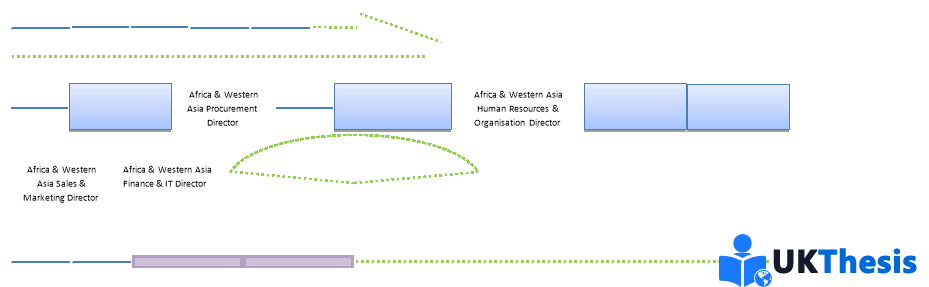
Author: Jacob Hood. Ref: (Audi AG, 2016)
Organogram Key:组织结构图键
Functional Relationship. Different Departmental Individuals/Functions that work very closely a together to achieve Organisational Objectives.
职能关系。为实现组织目标而紧密合作的不同部门个人/职能部门。
Line Relationship. Organogram structural links indicating hierarchal structure and a subordinates/superiors across departments.
直线关系。表示层级结构和跨部门的下属/上级的组织结构链接。
Functional Relationship. Symbol to indicate the whole department works loosely albeit of lesser importance as with all other business functions. Indicated with a symbol to maintain clarity of [Figure 1].
职能关系。表示整个部门工作松散的符号,尽管与所有其他业务职能相比重要性较小。用符号表示,以保持[图1]的清晰度。
Lateral Relationship. Different Departmental Individuals/Functions of the same ‘Hierarchal Position’ that a work very closely together to achieve Organisational Objectives.
横向关系。同一“层级职位”的不同部门个人/职能部门密切合作,以实现组织目标。
2.1.2 Overview of Operations Management Within Audi AG 奥迪公司运营管理概述
To gauge an understanding of the Key Operational Functions within Audi AG; an explanation of Operations Management in a broader sense and how the Business Function operates within organisations is critical. Joseph Martinich devised definitions in relation to Operations Management, “Operations management is a discipline and profession that studies (and practices) the process of planning, designing and operating production systems and subsystems to achieve the goals of the organisation.” (Martinich, 1997) It is responsible for all the processes associated with the design, planning, control, and production of the products/services that the organisation offers. Operations Management forms the fundamental groundwork of the production of products within organisations; and an efficient Operations Management Function leads to increased profitability, productivity and a more streamlined product build process. Within Audi AG, the key operations of the organisation involve the production of their various car models across the globe. These vehicles have numerous variations and are broadly bespoke based upon the customer’s desired specifications at the point of order. Some of these include: Different Body Shapes, Chassis, Engine Sizes, Left/Right Hand Drive, Transmission, Interior Specifications, Leather Seats, Carbon Fibre Trims etc. (Audi AG, 2016) These variations field complications to the Operations Management Team due to the fluctuating build times between variation of Model/Specification and requires careful scheduling and planning alongside the engineering and manufacturing processes in place to deliver the finished output/product.
本篇dissertation评估对奥迪公司关键运营职能的理解;从更广泛的意义上解释运营管理以及业务职能部门如何在组织内运作至关重要。Joseph Martinich设计了与运营管理相关的定义,“运营管理是一门研究(和实践)规划、设计和操作生产系统和子系统以实现组织目标的过程的学科和专业。”以及组织提供的产品/服务的生产。运营管理是组织内部产品生产的基础;高效的运营管理职能提高了盈利能力、生产力和更精简的产品构建流程。在奥迪公司内部,该组织的主要业务涉及在全球范围内生产各种车型。这些车辆有许多变体,并根据客户在订购时的期望规格进行广泛定制。其中包括:不同的车身形状、底盘、发动机尺寸、左/右舵驾驶、变速器、内部规格、真皮座椅、,碳纤维装饰件等由于型号/规格变化之间的制造时间波动,这些变化给运营管理团队带来了复杂性,需要在工程和制造流程的同时仔细安排和规划,以交付成品/产品。
2.1.3 Key Operations/Operations Functions Within Audi AG 奥迪的主要运营/运营职能
The Operations Management Function, which is known as the Production & Logistics & Procurement Functions within Audi AG are responsible for the design, control and delivery of Audi AG’s Key Operations (Production of Audi Vehicles). The Board of Management Member for the Production & Logistics Function is Dr.-Ing. Hubert Waltl and Procurement Board of Management Member is Dr Bernd Martens. (Audi AG, 2016) The inter-relationship between these two functions is crucial to the success of the Operational Processes at Audi AG especially within the ‘Logistics & Inventory Management’ Aspect of the Manufacturing Process. The Key Operational Functions and how Audi AG dissects these functions into Departments within Audi AG is indicated below. The assumptions below are taken from the Neckarsulm, Mid-South Germany Plant, where the production of Audi A4, A5, A7, A8, R8, RS6 and all the individual variations of such vehicles within the Neckarsulm Production Plant. (Audi AG, 2016)
运营管理职能部门,即奥迪公司的生产、物流和采购职能部门,负责奥迪公司关键运营(奥迪汽车生产)的设计、控制和交付。生产和物流职能的管理委员会成员是Ing.Hubert Walterl博士,采购管理委员会成员为Bernd Martens博士。这两个职能之间的相互关系对于奥迪公司运营流程的成功至关重要,尤其是在制造流程的“物流和库存管理”方面。关键运营职能以及奥迪公司如何将这些职能分解为奥迪公司的各个部门如下所示。以下假设来自德国中南部内卡苏尔姆工厂,奥迪A4、A5、A7、A8、R8、RS6的生产以及内卡苏尔姆生产工厂内此类车辆的所有单独变体。
Scheduling. The Operation Function of ‘Scheduling’ is responsible for the design and allocation of resources and setting up the timetable of when the product/service will be completed, following a customer order. (Management Study, 2017) Within the Organisational Context at Audi AG, they name this departmental function ‘Production Control & Planning’. (Audi AG, 2016) They utilise sophisticated computerised systems to ascertain the duration of time that it takes to fully manufacture the product dependent on current ‘Queue Time’, Model & Bespoke Specifications etc. This is then relayed to the Customer to give them an indication of the anticipated delivery time of their Audi Vehicle. A key aspect of ‘Scheduling’ is devising the algorithms and the systems based upon their research of previous ‘Build Time’ of vehicles to create accurate schedules for various models and variations of those models. Scheduling is also responsible for maximising the efficiency of the Production Line, Streamlining Processes and Eradicating Bottlenecks. For Example, within Audi AG the body and chassis of an Audi A4 takes sufficiently longer than the interior. Therefore, a key improvement to mitigate this issue could be to build in a buffer of excess Audi A4 bodies being manufactured in the night shift. This will then sufficiently mitigate the issue that the Interior aspects of the Manufacturing Process take less time to complete than the Exterior Production. Thus, maximising the number of vehicles that can be manufactured within a given time period.
日程安排。“调度”的运营职能负责资源的设计和分配,并根据客户订单制定产品/服务何时完成的时间表。在奥迪公司的组织背景下,他们将该部门职能命名为“生产控制与规划”。(他们利用先进的计算机系统,根据当前的“排队时间”、车型和定制规格等,确定完全生产产品所需的时间。然后将此信息传达给客户,以指示其奥迪汽车的预期交付时间。“调度”的一个关键方面是根据他们对以前车辆“建造时间”的研究来设计算法和系统,为各种模型和这些模型的变体创建准确的调度。调度还负责最大限度地提高生产线的效率,简化流程并消除瓶颈。例如,在奥迪公司,奥迪A4的车身和底盘比内饰要长得多。因此,缓解这一问题的一个关键改进措施可能是为夜班生产的多余奥迪A4车身建立缓冲区。这将充分缓解制造过程的内部方面比外部生产需要更少的时间来完成的问题。因此,最大限度地增加在给定时间段内可以制造的车辆数量。
Capacity Management. “Capacity Management is concerned with the matching of the capacity of the operating system and the demand placed upon that system.” (Wild, 2002) Capacity Management within Audi AG is part of the ‘Production Control & Planning” Departmental Function with the core objectives being to manage the current level of resources available in relation to the demand placed upon those processes; to deliver efficient and effective mechanisms that successfully meet Business Objectives. Capacity Management must be able to accurately draw upon historical and forecasted data to ascertain whether the current structure and configuration of Human/Non-Human Resources can sufficiently deal with current and prospective consumer demand. (Management Study, 2017) For example within Audi AG, they must be acutely aware of the Micro/Macro Environmental Factors, Sales Forecasts and balance these with a detailed analysis of the Production/Manufacturing Systems and make informed decisions as to whether internal operational adjustments are required. One of Audi AG’s Business Objectives is to work to ensure that the consumer doesn’t have to wait extensive quantities of time to receive their new Audi Vehicle. Short-Term Demand can be dealt with by increasing the forecasted build time from 6 weeks to 8 weeks. However, if there is a prolonged increased demand for a model of Audi Vehicle, whereby Customers must wait over 8 weeks for their new vehicle; it may be necessary to increase the amount of resources available to manufacture more units of that model (More Labour, Machines Etc.), to successfully meet business objectives. It is the role of Capacity Management to monitor the current trends in relation to the processes and make pragmatic strategic decisions based upon this data.
容量管理。“产能管理涉及操作系统的产能与系统需求的匹配。”奥迪公司的产能管理是“生产控制与规划”部门职能的一部分,其核心目标是管理与这些流程需求相关的当前可用资源水平;提供高效有效的机制,成功实现业务目标。能力管理必须能够准确地利用历史和预测数据,以确定人力/非人力资源的当前结构和配置是否能够充分满足当前和未来的消费者需求。例如,在奥迪公司内部,他们必须敏锐地意识到微观/宏观环境因素、销售预测,并通过对生产/制造系统的详细分析来平衡这些因素,并就是否需要内部运营调整做出明智的决定。奥迪公司的业务目标之一是努力确保消费者不必等待很长时间才能收到他们的奥迪新车。短期需求可以通过将预测的构建时间从6周增加到8周来处理。但是,如果对奥迪车型的需求长期增长,客户必须等待8周以上才能买到新车;可能有必要增加可用于制造该型号的更多单元的资源量(更多的劳动力、机器等),以成功地实现商业目标。能力管理的职责是监测与流程相关的当前趋势,并根据这些数据做出务实的战略决策。
Transformation Process. The Transformation Process is the Operational Function that addresses the process of taking ‘Inputs’ which include ‘Transforming Resources’ (Staff, Machinery) and ‘Transformable Resources’ (Raw Materials) and turns these resources/materials into finished ‘Outputs’ that are ready to distribute to the consumer. (Pearson, 2016, p.567) See Appendix A for the Transformation Process Model in a visual format. Within the Situational Context at Audi AG, the Transforming Resources include: Production Line Workforce, Machinery and Individual Plants. The Transformable Resources include: Raw Materials such as ‘Vehicle Body/Chassis’, ‘Engines’, ‘Leather Interior’, ‘Electronic Chips’ etc. The Output is the finished Audi Model Vehicle that is distributed to the customer, For Example ‘Audi TT.’ The Transforming Resources assist to construct/transform the Transformable Resources into the final output product. (Pearson, 2016, p.567) At Audi AG, there are a couple of functions responsible for implementing the Transformation Process efficiently and effectively, these being ‘Production Engineering’ and ‘Maintenance Engineering’ and ‘Quality Management’. Production Engineering is responsible for devising innovative processes that can streamline the Transformation Process of producing an Audi Vehicle, thus saving significant costs if these can be implemented effectively. Maintenance Engineering is responsible for the continued operations of seeing through the existing Engineering Processes attributed to building Audi’s vehicles. This needs to be done effectively to ensure that quality products are being produced to the correct schedule set out by the ‘Scheduling’ Function. Quality Management is responsible for the checking and vetting of the finished outputs to ensure it is to Audi AG’s quality specifications. This is crucial to offer a consistent quality of product and ensure customers are happy with the products they receive. (Audi AG, 2016)
转型过程。转化过程是指处理“输入”过程的运营职能,包括“转化资源”(员工、机械)和“可转化资源””(原材料),并将这些资源/材料转化为成品“输出”,准备分配给消费者。可视化格式的转换过程模型见附录A。在奥迪公司的情境背景下,转型资源包括:生产线劳动力、机械和个体工厂。可转换资源包括:原材料,如“车身/底盘”、“发动机”、“皮革内饰”、“电子芯片”等。输出是分配给客户的成品奥迪车型,例如“奥迪TT”。转换资源有助于将可转换资源构建/转换为最终输出产品。在奥迪公司,有几个职能部门负责高效实施转型过程,即“生产工程”、“维护工程”和“质量管理”。生产工程部负责设计创新流程,以简化奥迪汽车的生产转型流程,从而在有效实施这些流程的情况下节省大量成本。维修工程部负责对奥迪车辆制造的现有工程流程进行持续操作。需要有效地做到这一点,以确保按照“调度”职能部门制定的正确时间表生产高质量的产品。质量管理部门负责检查和审查成品,以确保其符合奥迪公司的质量规范。这对于提供始终如一的产品质量并确保客户对他们收到的产品感到满意至关重要。
Logistics & Inventory Management. “Inventory Management supervises the flow of goods from manufacturers to warehouses and from these facilities to point of sale.” (Manufacturing Tech, 2017) Within the Organisational Context at Audi AG, the Operations Management Function of Inventory Management is incorporated within the Logistics Department. Inventory Management is responsible for supervising the process of managing inventory at various degrees/levels of completion/processing of those materials from Raw Materials through to Finished Products. Inventory Management’s primary objective is to minimise the amount of excess capital that is expended on surplus inventory; the storage, transport and management of such inventory is very costly to organisations. Other reasons behind the implementation of this process is to be able to successfully meet seasonal demand, variation in production demand, ability to take advantage of quantity discounts, highlight quality/other issues in the Production Line and to streamline the Production Process and reduce costs. (Management Study, 2017) Within Audi AG, the Logistics Function must ensure to manage their inventory of Raw Materials (Engine Parts, Interior Materials, Chassis Etc.) so that they do not have excess Inventory costing the business money through unnecessary storage of such materials. Audi AG implement an Operational Approach called Just-In-Time (JIT) which will be explored in detail below, however broadly speaking it ensures the delivery of materials from Suppliers at precisely the time at when they are required in the Production Line. This program is devised in association with the Scheduling Function and mitigates the risk of unnecessary Raw Materials Inventory. Audi AG also must contend with the matter of ‘Finished Goods Inventory’ (Completed Vehicles). The approach within Audi AG is to ensure to sell such stock as quickly as possible while the vehicles are worth the most money, often through promotions on certain models and incentives to purchase the Models/Variations whereby there is excess ‘Finished Goods Inventory’. (Management Study, 2017) Audi also removes this form of inventory through offering the vehicles as Company Cars or through Employee Centred Incentive Schemes. (Audi AG, 2017) It is the role of Inventory Management to also prevent these occurrences from happening and analysing Sales Trends & Forecasts to minimise excess ‘Finished Goods Inventory’; as the costs to store and the depreciation of the vehicles reduces the profitability of the organisation.
物流和库存管理。“库存管理监督货物从制造商到仓库以及从这些设施到销售点的流动。”在奥迪公司的组织背景下,库存管理的运营管理职能并入物流部。库存管理负责监督从原材料到成品的各种完工/加工程度/水平的库存管理过程。库存管理的主要目标是最大限度地减少用于剩余库存的超额资本;此类库存的储存、运输和管理对组织来说成本高昂。实施该流程的其他原因是能够成功满足季节性需求、生产需求的变化、利用数量折扣的能力、突出生产线中的质量/其他问题,以及简化生产流程和降低成本。在奥迪公司内部,物流职能部门必须确保管理其原材料库存(发动机零件、内饰材料、底盘等),以免因不必要的材料储存而产生多余的库存成本。奥迪公司实施了一种称为适时制的运营方法,下文将对此进行详细探讨,但从广义上讲,它确保供应商在生产线需要材料的时候准确交付材料。该程序是与计划功能相关联设计的,可降低不必要的原材料库存风险。奥迪公司还必须处理“成品库存”(整车)问题。奥迪公司的方法是确保在车辆价值最高的情况下尽快出售此类库存,通常是通过对某些车型的促销和购买存在过量“成品库存”的车型/变体的激励措施。奥迪还通过将车辆作为公司汽车或以员工为中心的激励计划来消除这种形式的库存。库存管理的职责是防止此类事件的发生,并分析销售趋势和预测,以最大限度地减少过剩的“成品库存”;因为储存成本和车辆折旧降低了组织的盈利能力。
2.2 Key Operational Approaches To Operations Management 运营管理的关键运营方法
2.2.1 Just-In-Time Philosophy/Theory 适时制原理/理论
The Just-In-Time Philosophy (JIT) is primarily used within Manufacturing/Retail focused organisations, however the theory can be applied across a range of different market sectors. Just-In-Time (JIT) refers to the process of the supply of materials, either from external suppliers or from other areas within the organisation, delivering the items to the relevant department/area of the business at precisely the time that they need it. The main objective being to achieve reduction and mitigation of surplus ‘raw materials’ within the organisation with a view to increasing productivity, (Toyota Global, 2017) “The art of ‘just-in-time’ production consists of keeping intermediate stock levels down to an absolute minimum, yet none the less having each part arrive at the predetermined point at precisely the right time.” (Audi, 2017) JIT is a Production Model where items are manufactured/created to meet demand, not created in surplus/advance of need. (Tech Target, 2017) Within the Organisational Context at Audi AG, implementing Just-In-Time within the Procurement Process can significantly streamline the Production-Line Process and lead to increased productivity. For Example, within Production Line A at Audi Neckarsulm Plant, Germany the Scheduling and Logistics Department will utilise sophisticated computer systems to ascertain the quantity of each product is required to produce a given number of cars per day i.e. (500 Michelin & 750 Continental Tyres Per Day). The suppliers for these tyres will then be allocated a precise time slot to deliver the items ‘Just-In-Time’ for when they are required in the Production Line Process. This can assist to eliminate waste, inconsistencies, unreasonable requirements thus resulting in increased productivity in the line. (Toyota Global, 2017)
本篇dissertation解释了适时制原理主要用于以制造业/零售业为重点的组织,但该理论可以应用于一系列不同的市场部门。适时制是指从外部供应商或组织内其他领域供应材料的过程,在他们需要的时候将物品交付给相关的业务部门/区域。主要目标是在组织内减少和缓解过剩的“原材料”,以提高生产力,“‘及时’生产的艺术包括将中间库存水平保持在绝对最低水平,但也要让每个零件在正确的时间到达预定的点。“JIT是一种生产模式,生产/创造物品是为了满足需求,而不是在过剩/提前需求的情况下创造。在奥迪公司的组织背景下,在采购流程中实施适时制可以显著简化生产线流程,提高生产力。例如,在德国奥迪内卡苏姆工厂的生产线A内,调度和物流部将利用复杂的计算机系统来确定每天生产给定数量的汽车所需的每种产品的数量,即。然后,这些轮胎的供应商将被分配一个精确的时间段,以便在生产线流程中需要时“及时”交付物品。这有助于消除浪费、不一致和不合理的要求,从而提高生产线的生产率。
2.2.1.1 Advantages of Applying Just-In-Time Philosophy (JIT)应用适时制的优势
– Lower Stock/Raw Materials Inventory results in a significant reduction in storage space which saves capital in rental and insurance costs. (Tutor2U, 2017)较低的库存/原材料库存会显著减少存储空间,从而节省租金和保险成本。
– As stock is only purchased when orders are placed, it results less working capital tied up in stock, which can be invested elsewhere in/outside the business. (Tutor2U, 2017)由于只有在下订单时才购买股票,这会减少库存中的营运资金,这些资金可以投资于企业内外的其他地方。
– Mitigates the issue of un-sold finished stock being produced due to sudden & non-forecasted increases in demand and prevents the risk of stock perishing due to it only arriving when it is needed to be used. This can increase Profitability within Audi AG due to unnecessary capital not being expended on wasted materials/stock. (Tutor2U, 2017)缓解了由于需求的突然和未预测的增长而产生的未售出成品库存问题,并防止了由于库存只在需要使用时到达而导致库存死亡的风险。这可以提高奥迪公司的盈利能力,因为不必要的资本没有花在浪费的材料/库存上。
-Drives higher standards on the Production Line and with Suppliers due to there being little room for error with Minimal Stock retained to account for errors on the Production Line and very precise Delivery Slots can ensure Supplier Standards are maintained, thus increasing Productivity of these aspects within Audi AG. (Tutor2U, 2017)在生产线和供应商中推动更高的标准,因为保留最低库存以解决生产线错误的空间很小,而且非常精确的交货时段可以确保保持供应商标准,从而提高奥迪公司这些方面的生产力。
2.2.1.2 Disadvantages of Applying Just-In-Time Philosophy (JIT)应用适时制的缺点
– Little/No Room for Error. This is a big contributing disadvantage to the system for both the Production-Line. Minimal stock is kept for re-working faulty products due to the implementation of this process, therefore a lot of pressure is placed on the Production-Line to get things right first time. (Tutor2U, 2017)几乎没有犯错的余地。这对两条生产线的系统都是一个很大的不利因素。由于该流程的实施,重新加工有缺陷的产品的库存保持在最低限度,因此生产线面临着第一时间做好工作的巨大压力。
-Heavily Reliant on Suppliers. Suppliers are allocated a small-time slot to deliver the correct amount of the product that is specified by the Scheduling and Procurement Functions. If they miss their slot, deliver incorrect quantity/type of materials this can cause the Production Line to falter, meaning less vehicles are made, productivity is decreased and in-turn profitability. (Tutor2U, 2017)严重依赖供应商。供应商被分配了一个小的时间段来交付计划和采购职能部门指定的正确数量的产品。如果他们错过了时间,交付的材料数量/类型不正确,这可能会导致生产线出现故障,这意味着制造的车辆数量减少,生产力下降,进而导致盈利能力下降。
-There is no spare finished stock to cater for unexpected increases in demand, however the flexibility of the system means that it can react quickly to demand changes. Albeit this will not be as rapid for the consumer as having finished stock ready to be distributed. (Tutor2U, 2017)没有多余的成品库存来满足需求的意外增长,但系统的灵活性意味着它可以对需求变化做出快速反应。尽管这对消费者来说不会像成品库存准备好分发那样迅速。
2.2.2Six Sigma 六西格玛管理
Six Sigma is a widely used Operational Approach towards Operations Management and is frequently applied within Manufacturing Businesses, however the fundamental processes also apply within businesses operating within the Service Industry. “The Purpose of Six Sigma is to reduce process variation so that virtually all the products or services provided meet or exceed customer expectations.” (DTI, 2017) Six Sigma adopts a very data driven, disciplined method for eliminating defects within processes and promoting business improvement within organisations. (iSixSigma, 2017) Within Audi AG, this could mean the Manufacture of a Car Model or the Service offered to customers throughout the Sales Process. (Audi AG, 2016) “Six Sigma is able to show quantitatively how a process is performing and to achieve ‘Six Sigma Status’, a process must not produce more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities.” (iSixSigma, 2017) Six Sigma is dissected into three core elements including: Process Improvement, Process Design/Re-Design & Process Management and will be explored below.
六西格玛是一种广泛使用的运营管理方法,经常应用于制造业企业,但基本流程也适用于服务业企业。“六西格玛的目的是减少流程变化,使提供的几乎所有产品或服务都能达到或超过客户的期望。”六西格玛采用了一种非常数据驱动、严格的方法来消除流程中的缺陷,并促进组织内的业务改进。在奥迪公司内部,这可能意味着在整个销售过程中制造车型或为客户提供服务。“六西格玛能够定量地展示一个过程是如何执行的,为了实现‘六西格玛状态’,一个过程每百万次机会中产生的缺陷不得超过3.4个。”六西格玛分为三个核心要素,包括:过程改进、过程设计/重新设计和过程管理,并将在下文中进行探讨。
2.2.2.1Process Improvement 过程改进
The Process Improvement aspect of the Six Sigma Model addresses the concept of improving existing processes with the ultimate objective of increasing the quality of product/service that the consumer receives and attainment of ‘Six Sigma Status’
六西格玛模型的过程改进方面涉及改进现有过程的概念,最终目标是提高消费者获得的产品/服务质量并达到“六西格玛状态”
本站提供各国各专业dissertation范文,dissertation代写以及dissertation写作辅导,如有需要可咨询本平台。
