供应链管理paper代写范文:Simulation in Logistics and Supply Chain

供应链管理paper代写范文-物流与供应链仿真。本文是一篇由本站提供的留学生供应链管理专业paper代写范文。本篇paper的主要任务是免除物流和供应链中模拟与计划和控制的关系。为了了解模拟是如何用于分析供应链绩效的,Paper对文献综述进行了批判性分析。本篇paper研究的主要重点是分析在供应链规划和控制方面模拟中使用的各种方法,以分析各种方法的利弊。以下内容就是本篇供应链管理paper代写范文,供参考。

Introduction:引言
The main task of this paper is to exemine how simulation is being used in logistics and supply chain (LSC) in relation to planing and control. In order to understand how simulation is being used to analyse the supply chain performance, a literature review was critically analyse. The main focus of this reserch was to analyse the various methods being used in simulation as regard the supply chain planing and control in order to analyse the benefit and contrain of the various method ( ).
A sample of problem in SC was identify and treated with one of the methods of simulation in order to measure the efficiency and effectivenes within SC. Conclusion was drawn which compares and contras both approch to measure the weakness and streagnth in diffrent circumstancies.
本篇paper以供应链中的一个问题样本为例,用模拟方法之一对其进行识别和处理,以衡量供应链的效率和有效性。
Problem Identification and Description 问题识别和描述
Litrature Review 文献综述
A review recently by Cid Yanez et al., (2009) Identified more comprehensive taxonomy of the different types of simulation wich ara: continuous, discrete, System Dynamics, Gaming, Agent, Artificial Intelligence, Virtual Reality etc. However, thier are quite of number of methods or techniqures used in planing accross supply chain, namely XML, Spreadsheet, Mathematical Modelling, Java, potal Software, Matlab, etc. In contrast Skiadas and Skiadas, (2009) argue that methods or techniqures like Spreadsheet, XML, Java and Genetic Algorithm were not actual simulation techniqure but rather are merely simple analysis tools and programming methods wich is categorised under Discrete Mathematical Model wich are static in nature. In the same vein Small et al., (2013) suggests that Discrete mathematical model is diffrent in nature because it try to find an optimal solution to a problem in the present rather than in the future. In view of DAVIS, EISENHARDT and BINGHAM, (2007) agrees that mathematical modelling techniqures cannot deal with dynamic and complex situiation expecially in gaining competative advantage through the supply chain network. This means that mathematical model or techniques is not considered as the best in dealing with real phenomenon. Example product demand forecasting. Conversely, Dynamic simulation modelling is regarded as poor modelling techniqures as it lacks the ability to handle too detailed LSC micro problems such as job sequencing (Longo, 2011). However as ponted out by Chopra and Mendl (2007) there are three basic supply chain simulation in planinig and control wich are: System Dynamics (SD), Discrete Event Simulation (DES), and Agent Based Modelling (ABM). Accordingly, Lorenz and Jost (2006) have identified these three basic types of simulation in supply chain planing and optimization, each problem has a particular approach being used to find optimal solution. In view of the defination provided by copra and mendl (2011) in relation to supply chain management decision making, identified two main problem namely; strategic and opertational wich can be tackled by these approch (i.e. SD, DES ABM). ( ) suggest that In order to make the right decision it is important to prepare them with appropriate planning and control.
Cid Yanez等人最近的一篇综述对不同类型的模拟进行了更全面的分类:连续、离散、系统动力学、游戏、代理、人工智能、虚拟现实等。然而,在跨供应链规划中使用了相当多的方法或技术,即XML、电子表格、数学建模、Java,potal Software、Matlab等。相比之下,Skiadas和Skiadass认为,电子表格、XML、Java和遗传算法等方法或技术不是实际的模拟技术,而只是简单的分析工具和编程方法,属于本质上静态的离散数学模型。同样,Small等人认为,离散数学模型本质上是不同的,因为它试图在当前而不是未来找到问题的最优解。鉴于DAVIS,EISENHARDT和BINGHAM,一致认为,数学建模技术无法处理动态和复杂的情况,尤其是在通过供应链网络获得竞争优势方面。这意味着数学模型或技术在处理真实现象时并不被认为是最好的。产品需求预测示例。相反,动态模拟建模被认为是较差的建模技术,因为它缺乏处理过于详细的LSC微观问题(如工作顺序)的能力。然而,正如Chopra和Mendl提出的那样,在规划和控制中有三种基本的供应链模拟:系统动力学(SD)、离散事件模拟(DES)和基于代理的建模。因此,Lorenz和Jost已经确定了供应链规划和优化中的这三种基本模拟类型,每个问题都有一种特定的方法来寻找最优解。鉴于copra和mendl对供应链管理决策的定义,确定了两个主要问题:;这些方法(即SD、DES ABM)可以解决战略和操作问题。建议为了做出正确的决定,重要的是要为他们做好适当的规划和控制。
Similarly, Arne Schuldt (2010) state that the primary supply chain function are applied in order to tackle challenges usually, each of the function is not sufficient alone to tackle the challenges instead multiple functions contributed by multiple techniques or model must be combine to supply network in order to make the right decision. For instance, Baril et al. (2016) use both approch to improve health care service delivery by reducing patient delay using DES, SD to improve patient pathways and ABM for quick implementation process. As can be seen both method can be used to achieve SC strategic and planning objectives
同样,paper引用Arne Schuldt的理论指出,应用主要供应链功能是为了应对挑战,通常,每个功能都不足以单独应对挑战,相反,必须将多种技术或模型贡献的多个功能组合到供应网络中,才能做出正确的决策。例如,Baril等人使用DES、SD改善患者路径和ABM快速实施过程,通过减少患者延迟来改善医疗服务提供。可以看出,这两种方法都可以用于实现供应链战略和规划目标
However, Lean thinking simulation and implementation has emerged in various segment of the suppy chain particularly in manufacturing and recently in the healthcare because, recent litrature has shown significant benefit such as increased patient and management throughput( ). In view of ( ) every oranisation has similar process of simulation implemetation wich must start with define value, measure, analyse, improve and control as indicated in the following figure 1
然而,精益思维的模拟和实施已经出现在供应链的各个环节,特别是在制造业和最近的医疗保健领域,因为最近的文献显示了显著的好处,如增加了患者和管理吞吐量。每一个创造有类似的模拟实施过程,必须从定义值、测量、分析、改进和控制开始,如下图1所示
Figure 1 Organisational Approch of Simulation
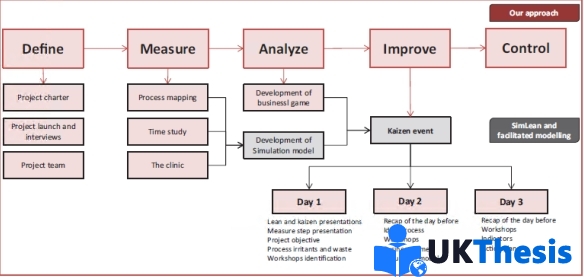
Source: (Baril et al. 2015)
STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES OF THE THREE (3) APPROACHES 三种方法的优缺点
System Dynamics 系统动力学
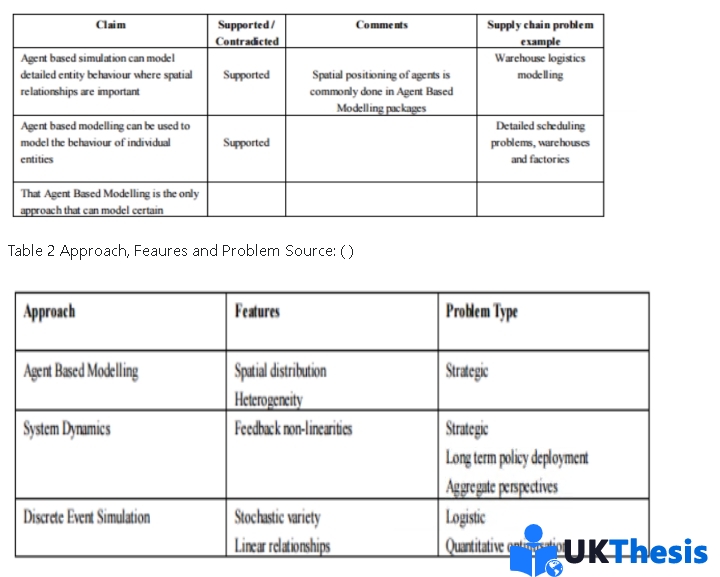
Despite the potential benefit and broad range of applications of SD in supply chain domains, the SD techniques is often regarded as a means suited to handle only macro SC problems and relational policy problems before implemetation ( ). Conversely, SD is regarded as a poor modelling technique but, as agued by ( ) that System Dynamics need to be complemented by micro modelling techniques in many situation, such as credible models which lies in the body domain of Descret event simulation that is strong and beneficial for analysing detailed and complex situaions. However, from its earliest to the recent reserch in SC ( ) has identified that feedback flow of information has been a core central features of SD and the techniques has been used to analyse many SC problems where studies finding suggested that SD is a continuous and syncronose procesess where operations are aggregated together rather than being as seprate or discrete entities. For This reason it has being suggests that the the SD techniques may be less effective to tackle problems where human behaviour or individul are observed. For example shoppers habit in Tesco. In the same vein, ( ) that one of the constraint of SD, is not effective to tracking movement of individual in space and location. In other word, one of the major aim of SC is targeted at individaul customer but, SD being a cyclical process may not model the movement of individual as it tend to varies from one point in time to another. For instance, the Impact of Brexit policy in the uk to Eu may have negative impact on various supply chain networks (Viner, 2016). Therefore, SD is aims only at addressing policy problems that are strategic in nature rather than tactical or operational level particularly dealing with human interaction in SC ( ). In contrast, many scholars in the field of SC claims that ABM can model detailed distinct behaviour where spatial relationships co-exist. And ABM can be used to model the behaviour of distict supply chain or distinct suppy node ( ). For example SD deals with problems like:
尽管SD在供应链领域具有潜在的好处和广泛的应用范围,但SD技术通常被认为是一种在实施前仅适用于处理宏观供应链问题和关系政策问题的方法。相反,SD被认为是一种较差的建模技术,但正如所困扰的那样,在许多情况下,系统动力学需要由微观建模技术来补充,例如位于Descret事件模拟主体领域的可信模型,该模型对于分析详细和复杂的情况是强大和有益的。然而,从最早到最近的SC研究已经确定,信息的反馈流一直是SD的核心核心特征,并且该技术已被用于分析许多SC问题,其中研究发现,SD是一个连续和同步的过程,其中操作被聚合在一起,而不是单独或离散的实体。因此,有人认为,SD技术在解决观察到人类行为或个体的问题方面可能不太有效。例如,特易购的购物者习惯。同样,SD的约束之一对于跟踪个体在空间和位置上的运动是无效的。换句话说,SC的主要目标之一是针对个人客户,但SD作为一个周期性过程,可能不会对个人的运动进行建模,因为它往往在不同的时间点有所不同。例如,英国脱欧政策对欧盟的影响可能会对各种供应链网络产生负面影响。因此,SD仅旨在解决战略性的政策问题,而不是战术或操作层面的问题,特别是处理SC中的人际互动。相比之下,SC领域的许多学者声称,ABM可以在空间关系共存的情况下对详细的不同行为进行建模。ABM可用于离散供应链或离散供应节点的行为建模。例如,SD处理以下问题:
Supply chain redesign 供应链重新设计
Quality perception and Quality Control 质量感知与质量控制
E-collaboration 电子协作
Impact of demand amplification on transport cost 需求放大对运输成本的影响
Cycle time compression and Performance metrics 循环时间压缩和性能指标
The effect of batching on bullwhip 配料对牛鞭的影响
Discrete Event Simulation (DES) 离散事件仿真
Base on litrature reviews, claims that DES is very effective to handle the problem of variation in time intervals ( ) In similar vein, DES in supply chain planing and control can be used to measure relationships between entities in it strategic form. For example……………………………. ( ) argue that DES is not very effective for modelling policy in it generic level. Of course in reality SC problems under critical study ranging from planing, operations, and strategy, a more embodied discription by many leading scholar in the field of SC emphasised the need of of DES in the operational and planing level whereby the DS is more practicable in application to strategic level problems ( )
基于文献综述,声称DES在处理时间间隔变化问题方面非常有效。类似地,供应链规划和控制中的DES可以用于以战略形式衡量实体之间的关系。认为DES在其通用级别上对政策建模不是很有效。当然,在现实中,从规划、作战和战略等关键研究中的SC问题,许多SC领域的领军学者更具体地描述了DES在作战和规划层面的必要性,从而使DS在应用于战略层面的问题时更具实践性
Agent base Simulation 基于Agent的仿真
Agent Based Modelling ABM is an emerging method of simulation capable of application throughout the range from the strategic to operational level in the supply chain Arvitrida, Robinson and Tako, (2015) . As an emerging model, a number of views have been made for ABM. For instance, agent base model of simulation can be use to exemine distinct behaviour where spatial interconnection of relationships core exiest ( ). Similarly, agent based simulation can be used to model the behaviour of individual characteristics and it has being term as the only techniqures that can model certain features such as “agilty” to respond to ever increasing level of volitality of deman, agility in the sense of quick response to what ever situation under study (Critopher, 2011 ). ABM deals with supply chain ploblem in the following:
基于Agent的建模ABM是一种新兴的模拟方法,能够在供应链的战略到运营层面应用。作为一种新兴的模式,人们对反导提出了许多看法。例如,模拟的基于代理的模型可以用于免除关系的空间互连最核心的不同行为。类似地,基于智能体的模拟可以用于对个体特征的行为进行建模,它被称为唯一可以对某些特征进行建模的技术,如对不断提高的需求者意志水平做出反应的“敏捷性”,对所研究的情况做出快速反应的敏捷性。ABM在以下方面处理供应链问题:
Market dynamics 市场动态
Modelling control elements 建模控制元素
Human behaviour on bullwhip effect 牛鞭效应下的人类行为
Human behaviour and trust 人类行为和信任
Collective customer collaboration 集体客户协作
Table 1 Agent Base Simulation Source: 表1基于Agent的模拟来源:
Discussion and Conclusion 讨论和结论
The review of the litrature in this paper point out the benefit and constraint. In other words, it differenciate the various method of simulation in sc perspective. It shows that the various method varies and differs in scope both in customs and in practice or reality. In particular, SD is predominantly regarded as static in nature as it involves in continuous process or vertual techniques to tackle macro supply chain problems that are strategic in nauture. On the other hand, both DES and ABM are complementry to model entities in the same supply chain to varioius supply networks.
本篇paper对文献进行了综述,指出了其优点和制约因素。也就是说,它从供应链的角度区分了各种模拟方法。它表明,无论是在习俗上,还是在实践或现实中,各种方法的范围都是不同的。特别是,SD在本质上主要被视为静态的,因为它涉及到解决宏观供应链问题的连续过程或实际技术,而这些问题在航行中具有战略意义。另一方面,DES和ABM都是对不同供应网络的同一供应链中的实体建模的补充。
However, the major challengies to be fully and critcally analyse by researchers remains on the ability to match DS and ABM to work together in order to tackle companies problem internally and externally.
然而,研究人员需要全面而标准地分析的主要挑战仍然是能否将DS和ABM相匹配,以便在内部和外部解决公司问题。
Thus, most supply network constrain related to timing is that, the time intended to find optimal solution mostly exceed the parameter of the time considered for executing the the SC respective function. This is more so for the fact that, static planning cannot be applied externally (I.e. outside the organisation) but rather internally, within the organisational boundaries of control as it involves continues or virtual process. Furthermore, the nature of ABM, in decision-making cannot be achieve using centralised approach because, not all information are centrally available.
因此,与时序相关的大多数供应网络约束是,旨在找到最优解的时间大多超过执行SC各自函数所考虑的时间参数。更重要的是,静态规划不能在外部(即组织外部)应用,而是在内部,在组织控制范围内应用,因为它涉及持续或虚拟过程。此外,ABM的性质,在决策中不能使用集中的方法来实现,因为并非所有信息都是集中可用的。
Finally, it may be possible in the future to identify maximal self-contained system within lager systems that can be centrally control at the same time re-planning in the continuous process. But most likely that system of computational complexity is likely to exists within the boundaries of one company.
最后,paper总结到,在未来可能会在更大的系统中识别出最大的自包含系统,这些系统可以在连续过程中进行重新规划的同时进行集中控制。但最有可能的是,这种计算复杂性的系统很可能存在于一家公司的边界内。本站提供各国各专业paper范文,paper代写以及paper写作辅导,如有需要可咨询本平台。