英国某大学留学生作业:国际商务基础之跨境贸易

IB Fundamentals, Lecture 3
国际商务基础,演讲3
Trading Across Borders
跨境贸易
Lecture Objectives
讲座目标
• Discuss the changing patterns of trade and how these impact on IB
讨论贸易格局的变化,以这些如何影响国际商务
• Present the main theories of international trade and discuss their relevance today
目前主要的国际贸易理论和今天讨论的相关
• Introduce the key objectives that determine governments’ trade policy
介绍政府贸易政策的主要目标
International Trade: an Introduction
国际贸易:介绍
• Trade is the oldest type of international business
贸易是国际业务的最古老的类型
• Trade liberalisation (particularly successful at multilateral level) has seen trade volume growing at a faster rate than the world GDP
贸易自由化(特别是在多边层面上的成功)的贸易额以更快的速度比世界GDP增长
• The nature of trade and its benefits vary among countries and regions of the world
不同的世界不同国家和地区之间的贸易的性质和它的好处
• Trade has significant impact on businesses, governments and society
贸易企业,政府和社会的重大影响
The Role and Characteristics of International Trade
国际贸易中的作用和特点
• Trading transactions may be in goods (merchandise trade) or services (commercial service trade)
• Merchandise tradeincludes agricultural products, fuel and mining, and manufactured goods
• Commercial servicesinclude finance, transport and technology.
• All countries need such goods and services, yet whether they produce or import them depends on
many factors such as natural resources and government policies
• Trade is seen as contributing to economic growth, hence few governments attempt to be self-sufficient today (‘autarky’)
Volume of World Merchandise Exports and GDP (annual percentage change), WTO Secretariat, Statistics 2010
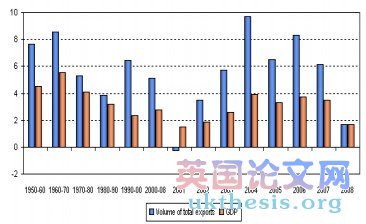
International Trade and World GDP
• Why trade volume often surpasses GDP?
- ….
• What is the trade openness index and what does it reveal?
- …
- ….
International Trade Data (WTO, Secretariat Statistics, 2010)
Value of merchandise exports, 2008: ….
Exports by destination: developed versus developing economies….
Exports by region: Europe, Asia, North America ….
Exports by main product groups (agriculture; fuel and mining; manufactured goods): ….
Exports by product group (fuels, other machinery, other chemicals, automotive products, other food products): ….#p#分页标题#e#
International Trade Data, 2010 (cont)
• The largest export product groups: fuels (18.2%), other machinery (12.4%) and other chemicals (8.1%); mainly exports from North America, Europe and Asia
• North America: intra-regional trade (50%), yet trade with the rest of the world is growing faster; top export products: other machinery (13.5%), fuels (12.4%) and automotive parts (10.3%)
• South and Central America: by destination, a shift from TRIAD to other regions; by product groups: fuels (27.2%); other food products (21.9%) and ores and minerals (9.5%)
International Trade Data, 2010 (cont)
• Europe: intra-regional trade (73%); top export products: other machinery (15.6%), automotive products (10.5%) and other chemicals (10.1%)
• CIS: intra-regional trade (19%); top export products: fuels (59.3%), iron and steel (9.5%) and other chemicals (5.8%); most fuels go to Europe (42.1%)
• Africa: exports to Europe, North America and Asia; by product groups: fuels (62.7%); other food products (4.6%) and non-ferrous metals (4.1%)
• Middle East: main exports destination Asia (56%); top export products: fuels (72.5%), other chemicals (5.2%) and other semi-manuf (4.7%); fastest growing product group: integrated circuits and pharmaceuticals
• Asia: intra-regional trade (50%); top export products: other machinery (13.4%), fuels (8.9%) and EDP (7.4%).
• Largest trading countries in merchandise and services:…
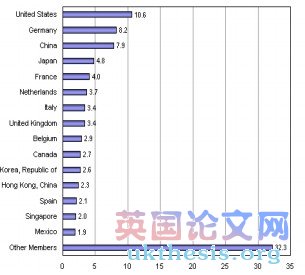
WTO Members’ Share in World Merchandise Trade, 2008
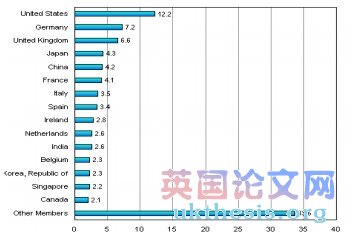
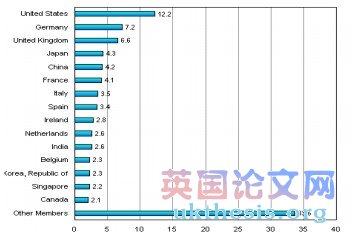
WTO Members’ Share in World Commercial Services Trade, 2008(percentage)
Exports of least developed countries by major product (percentage of total volume; WTO Secretariat, 2010)
Patterns of Global Trade
• Major industrialised countries of the TRIAD have dominated trade in the post-war period, but this pattern is breaking down
• Developing and transition economies have increased their share of world trade
• There are exceptional performers:
- the rise of export-oriented manufacturing (e.g. China)
- the growing importance of resource-rich exporting (e.g. Middle Eastern countries)
• The least developed countries, most of them in Sub-Saharan Africa, have fallen behind
Conclusions
• International trade generates wealth for countries and businesses, while satisfying consumer needs for products and services
• Emerging countries are now gaining on the established developed countries in their share
of world trade• Governments often intervene in trade in order to promote a variety of national objectives and, in doing so, they rely on a wide array of tools (trade instruments) to influence the#p#分页标题#e#
composition and volume of trade
http://www.ukthesis.org/thesis_sample/
Recommended Readings for this Lecture:
• J. Morrison (2009) International Business: Challenges in a Changing World. London: Palgrave Macmillan, Chapter 6 “International trade and regional integration”, 195-235.
• R. Sally (2008) Trade Policy, New Century: the WTO, FTAs and Asia Rising, London: The Institute of Economic Affairs, Hobart Paper 163
• W. Martin and A. Mattoo (2010) “The Doha Development Round: what’s on the table?”, Journal of International Trade and Economic Development19, 1, 81-1-7.
• R. Vernon “International investments and international trade product life cycle”, Quarterly Journal of Economics, 1966, May, 190-207
• B. Snowdon and G. Stonehouse (2006) “Competitiveness in a globalised world: Michael Porter on the microeconomic foundations of the competitiveness of nations, regions and firms”, Journal of International Business Studies37, 2, 163-75.